Leak integrity implies safety: Pressure measurement of pipelines
Below our feet is a vast, branch-like infrastructure without which commerce and society would cease to function. Millions of kilometers of pipelines transport natural gas, biogas and fresh and waste water from producers to consumers. Especially for those more hazardous materials like gas, safety plays an enormous role. Resource losses and environmental pollution can equally also result from leaking pipes. UNION Instruments has now developed a pressure test kit, which will henceforth simplify leak testing many times over. Pressure measurement cells made by STS are also employed in this kit.
The pressure test kit, PMS3000, from UNION Instruments GmbH was developed for implementing all essential process steps in the leak testing of pipelines consistently, by employing the matched components of a single testing system.
The fields of application are diverse:
- gas supply according to DVGW G469-(A) A2, B2, B3, C3 and D2
- potable water supply according to DVGW W400-2, Part 16
- technology, industry, process technology
- district heating pipelines
- geothermal sensors
- cable conduits
- sewer pipes

Figure 1: Pressure test kit PMS3000 (Source: UNION Instruments)
At this point, we would like to concentrate on the leak testing of potable water pipelines by the so-called contraction process (also termed ‘contraction pressure testing’). The test medium in this instance will be water.
The contraction process in potable water supply
Potable water supply is often performed with plastic piping. If a high test pressure is applied, this will result in a volume increase. This expansion in turn causes a pressure drop, which makes leak testing more difficult. Additionally, it must be ensured that the pipeline to be tested is sufficiently air-free. The specialist contraction procedure ensures that a correct leakage assessment can be given here. The norms for this are set out in DVGW Worksheet W400-2, Part 16.
To perform the contraction process according to W400-2, Part 16, besides the PMS3000 pressure test kit, the DAK2000 pressure relief kit is also needed, so that the water volume to be discharged can be centrally recorded independent of the output volume and then relayed to the PMS3000. It is through this direct linking that manual exertion can be reduced and transmission errors avoided. To build up pressure, a pump is additionally essential. In this respect also, UNION Instruments has various solutions available which are matched to the PMS3000.

Figure 2: Contraction process according to W400-2, Part 16
Source: UNION instruments
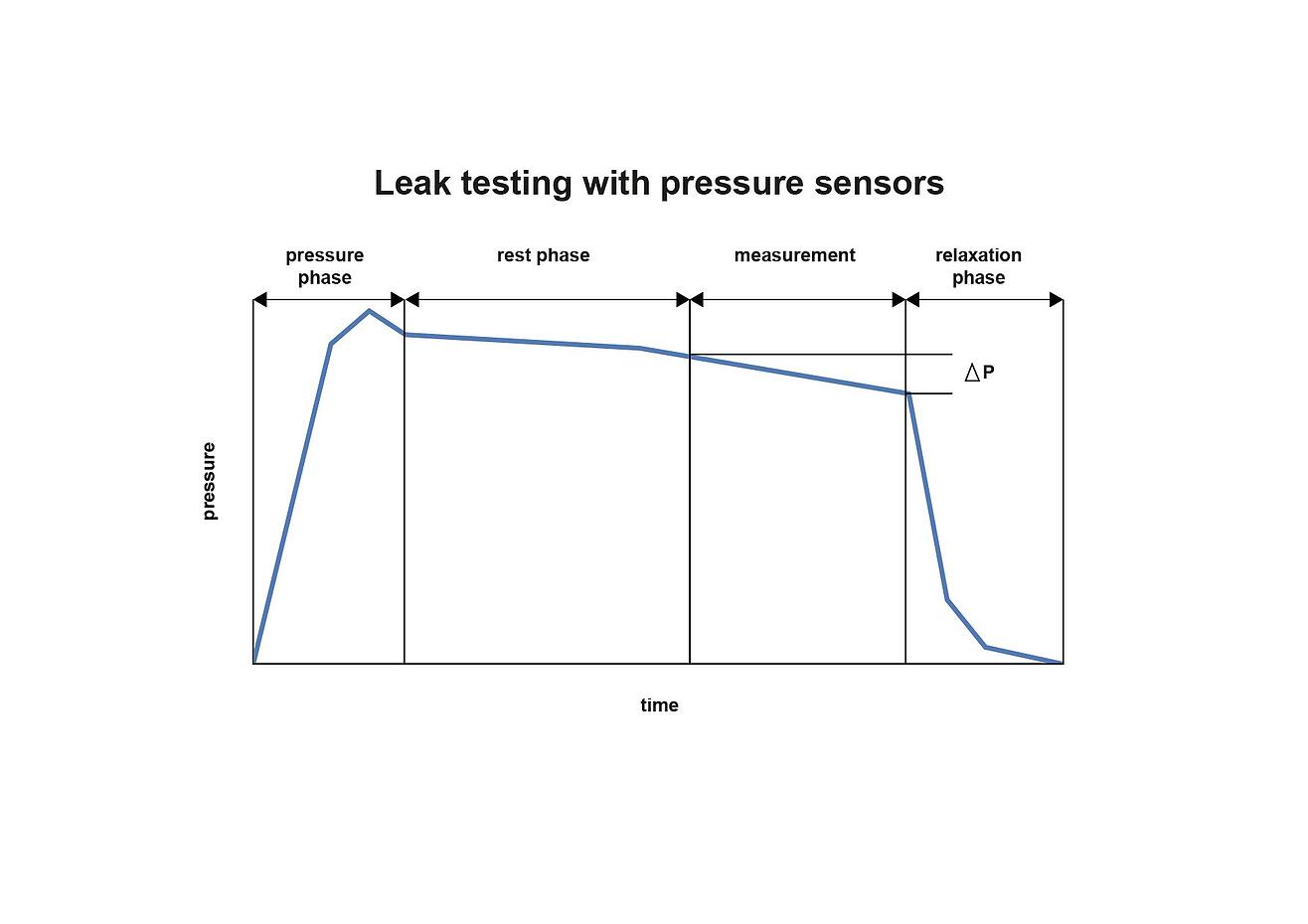
The contraction process (see Fig. 2) is relatively complex and takes place over several phases. The leak test itself extends over 3 to 4 hours. Using the PMS3000, the process is divided into seven phases. In the first phase, the relaxation phase, the static water pressure and pipe temperatures are measured. Next begins the pressure build-up phase. Here the test pressure is reached, which is about 4 bar higher than the operating pressure. This phase is completed within ten minutes. The rate of pressure rise can be observed with the PMS3000, thus allowing an initial evaluation of air-absence.
Once the test pressure is attained, the pressure maintenance phase then begins. Pressure preservation is achieved here by continuous re-pumping. In the following rest phase, the fall of pressure and thus the pressure reduction as a percentage of the test pressure is observed: The pressure here may not fall by more than 20 percent.
Next comes pressure reduction for testing air-absence. Water is released here, whose flow volume is measured and relayed to the PMS3000. This discharged water volume should be accompanied by a certain pressure fall. Should this not be the case, then too much air was present in the pipeline tested.
Once this phase is over, the 30-minute main test can begin. At this point, pressure is once again applied to the pipe. Should a fall in pressure occur here, then the main test will be extended to 90 minutes. Over this timeframe, the pressure in the pipe may not decline by more than 0.25 bar, otherwise the pipe would be deemed leaky.
This entire test process is stored on the SD card of the pressure test kit and is available as a PDF report requiring no further evaluation software from the user.
For its pressure measurements, the PMS3000 is equipped with a piezoresistive pressure transducer from STS. Since this pressure test kit is used in various applications, the demands upon these measuring cells are very high. They must be able to display a pressure range from just a few mbar up to 1,000 bar (leak testing hydraulic systems, for example) and yet still perform highly precisely. Among the requirements set out by UNION Instruments for STS was a stability of 5 mbar over ambient air temperature changes of 15 kelvin at test pressures ranging from 20 to 25 bar. For more on the integration of piezoresistive measuring cells into existing applications, please see here.
Characteristics of the PMS3000 system in brief:
- robust, waterproof and on-site-ready pressure test kit
- integrated report printer
- colored-graphics touch display
- 32 GB SD memory card, mobile readable over USB
- various external connectors
- test procedures of DVGW guidelines G469 (A) : 2010 and W400-2 : 2004 stored in-device
- complete array of connection components and test pumps for pressure build-up available
- integrated piezoresistive transducer from STS with a pressure range of 100 mbar to 1,000 bar (accuracy: ≤ ± 0.50 / 0.25 % FS)